Gynecological surgeries
Experienced surgeons
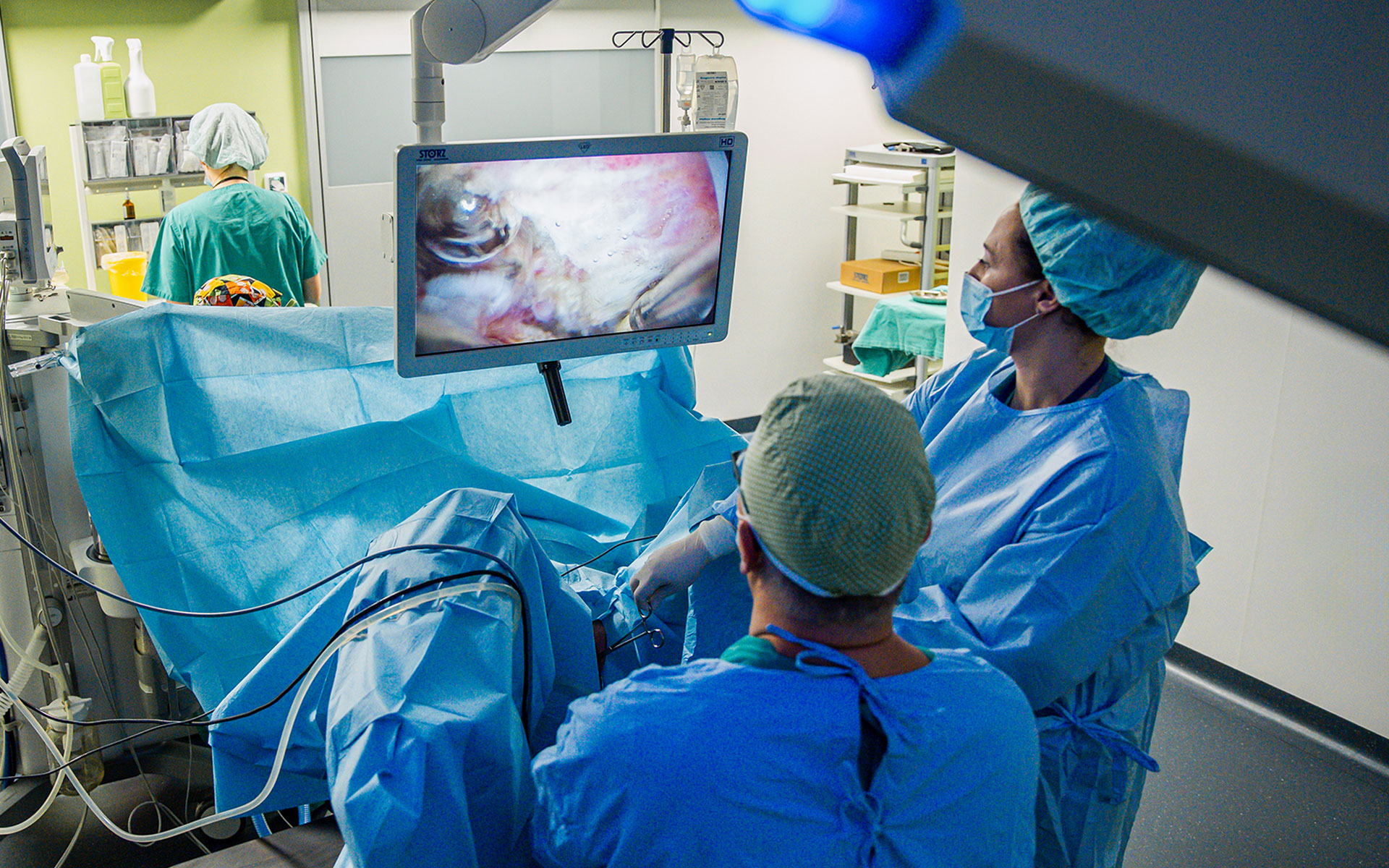
In two modernly equipped operating rooms at the only private maternity and gynecology hospital in Croatia, the specialists at Podobnik Hospital perform all types of major gynecological surgeries: removal of fibroids, cystic ovarian formations, removal of the uterus or surgical treatment of urinary disorders and uterine prolapse. Minor gynecological procedures are also performed like curettage, vacuum aspiration of the uterus, corrective vaginal and genital plastic procedures, and minimally invasive surgeries including laparoscopy and hysteroscopy. The team of experienced gynecological surgeons at Podobnik Hospital, together with the anesthesiologists, operating nurses and other medical staff, will perform a surgical procedure and postoperative recovery according to each patient’s individual needs.
Types of surgeries
ABDOMINAL HYSTERECTOMY (REMOVAL OF THE UTERUS)
An abdominal hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia. Before the procedure, the bladder is emptied by introducing a urinary tube, called a catheter, through the urethra. The catheter usually remains in the bladder for 2 to 3 days. After washing and disinfecting the surgical field, the doctor opens the abdominal wall with an incision just above the pubic hair line. The uterus is separated from the neighboring organs and certain blood vessels are ligated. After that, the uterus is removed in its entirety, with or without ovaries, and sent for histopathological specimen examination.
VAGINAL HYSTERECTOMY
A vaginal hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which the uterus is removed through a cut in the vagina. Indications for a vaginal hysterectomy largely coincide with indications for an abdominal hysterectomy, but this procedure is technically more demanding. On the other hand, the patient's recovery and hospitalization are significantly shorter compared to the recovery of patients who undergo abdominal hysterectomy. Pročitajte više
Urination disorders are a problem for almost half of women over 50. 25-30% of them suffer from static or stress urinary incontinence (SUI). In the treatment of SUI, trends include placing polypropylene strips under the middle third of the urethra (midurethral slings), and in the treatment of pelvic floor defects, in addition to classic surgical methods that use native tissue, we also use top-quality titanium-coated polypropylene meshes. With these methods, the duration of hospitalization is significantly shortened, full quality of life and work capacity are established faster, damage to the surrounding tissue is minimal, and the connection of the executive and sensory organs with nerves remains intact. Treatment of a prolapse is a surgical method, while static incontinence can be treated conservatively and surgically. There are more than a hundred surgical methods of treating SUI. Pročitajte više.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed when it is necessary to find the cause of pelvic problems that cannot be diagnosed by gynecological examination, ultrasound or related examinations. It can be performed in cases of acute and chronic pain, suspected ectopic pregnancy, and it is an especially important examination method in the treatment of infertility.
Operative laparoscopy is a common method in ovarian cyst surgery (cystectomy), tubal ligation (sterilization), diseased fallopian tube extraction (salpingectomy), and fibroid extraction (myomectomy). Additionally in cases where the pregnancy is in the fallopian tube, ectopic pregnancy surgery with (salpingectomy) or without extraction (salipingotomy) of the altered fallopian tube. Pročitajte više.
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that enables a detailed examination of the inside of the uterus. It is performed using a hysteroscope with a video camera attached to it (a kind of a narrow telescope), and it is introduced through the cervix into the uterine cavity. Through the hysteroscope, a special solution is introduced into the uterine cavity during the procedure, which expands the walls of the uterus thus providing the best possible view of the interior. Hysteroscopy can be diagnostic or therapeutic.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy lasts a few minutes and is performed on an outpatient basis, under short-term anesthesia. The procedure is performed in order to carry out fertility assessment in case of repeated miscarriages, irregular and heavy menstrual bleeding, irregular bleeding in peri- and post-menopause, and to check the uterine lining in women who are taking some kind of medicine for breast cancer. In some cases, at the end of the procedure, it is necessary to take a tissue sample of the uterine mucosa and carry out a histopathological analysis. Pročitajte više.
We perform all types of vaginal and plastic surgeries. Front and back vaginal plastics surgeries are most often performed as part of vaginal hysterectomies, in order to completely eliminate the genital system issues and restore its function.
- Removal of the hymen or vaginal introitus stenosis
- Surgical correction of the birth canal after childbirth and episiotomy
- Labiaplasty, reducing the size of the labia minora
Genecology specialists are experts for plastic surgeries of the genital system as they know the anatomy, function and morphology of that region best, along with all the changes in a woman's life stages. We perform all surgeries in the operating room under general anesthesia.
-
 all types of gynecological procedures and surgeries
all types of gynecological procedures and surgeries
-
 minimally invasive surgery – HSCP and LPSC
minimally invasive surgery – HSCP and LPSC
-
 all small procedures are performed in the operating room under general anesthesia
all small procedures are performed in the operating room under general anesthesia
-
 24-hour medical care in single room suites
24-hour medical care in single room suites
Operating rooms
The hospital has two modernly equipped operating rooms:
An operating room for endoscopic surgeries with STORZ equipment for laparoscopy and hysteroscopy for a number of procedures - from diagnostic hysteroscopy (during infertility treatment) to more complex procedures of operative resectoscopy of polyps and fibroids inside the uterus. Ovarian tumors and fallopian tube surgeries are most often performed laparoscopically as well as surgically more demanding procedures such as laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomies.
An operating room for major gynecological surgeries - from vaginal and abdominal hysterectomy to operative treatment of urinary disorders, uterine prolapse and vaginal plastic surgeries. All procedures are performed under spinal or general endotracheal anesthesia. Constant postoperative care and supervision of patients in the inpatient care unit are provided with 24-hour medical care.
Minor gynecological procedures
There are several reasons for performing dilatation and curettage:
- Dilation, vacuum aspiration of the uterus and curettage (DVAC) are performed to remove a failed pregnancy or residual products of pregnancy in case of impaired fetal development/failed pregnancy or after a miscarriage.
- Dilation, vacuum aspiration of the uterus and curettage (DVAC) are performed in the case of termination of pregnancy and intentional abortion (abortus artificialis).
- Diagnostic curettage is most often performed due to irregular bleeding from the uterus in women of mature age. Tissue is removed from the uterus because such tissue can undergo hormonal or inflammatory transformation, benign or malignant.
- Therapeutic curettage is performed due to various uterine bleedings that do not respond to medical therapy. To make a final diagnosis, the obtained tissue from the uterus is sent for pathohistological analysis.
Conization or cold knife cone is a surgical procedure which involves the excision (using scalpel) of a cone-shaped portion of the cervix where changes were found. As a rule, conization is performed under general anesthesia, and the patient stays to recover in the hospital after the surgery for three to four days. Cold knife conization is a surgical method primarily used for diagnosis, and most often as a therapy for certain conditions. The final diagnosis is made by the pathologist, through a serial microscopic examination of the removed specimen. The pathologist also assesses the involvement of the cone edges and tip, which is an important prognostic factor for the patient's final healing.
Although conization is not a major surgical procedure in terms of its scope, the risk of complications is relatively high. The most common early complication is bleeding, which occurs in 6-7% of the cases. Some patients (about 4%) may later have problems with conception, miscarriage or preterm labor (1%). After removing the cone, the so-called cervical plastic surgery is performed to model the remaining part of the cervix and reduce the possibility of postoperative bleeding.
LETZ is a procedure which is performed to remove the transformation zone of the cervix by using a low-voltage "diathermy loop" - an electric loop. This creates a cut and coagulation along the cut line. In everyday use, the term LETZ refers to the technique itself (application of an electric loop) which removes the transformation zone, to LETZ biopsy, i.e. taking samples from any part of the cervix, and to LETZ conization, i.e. removing a cone-shaped part of the cervix.
With the LETZ procedure, the cervix is spared, because the incision is not deep, and only the surface tissue is removed. Moreover, it is only after the procedure and pathohistological examination of the removed tissue that it is possible to accurately determine whether the lesion has been completely removed. Given that the high-frequency current coagulates the blood vessels, bleeding during the procedure is scarce, and no cervical plasty is necessary. Because it is minimally invasive, this method is especially recommended for women who have not given birth yet.
Cysts of the Bartholin's gland located at the bottom edge of the labia majora occur as a result of previous inflammatory processes or scars after a trauma, which lead to blockage in the outlet duct of the gland and accumulation of secretions. A secondary bacterial infection of the secretions causes acute inflammation (Bartholinithis) accompanied by severe pain and redness. At that stage, it is possible to cure by using broad-spectrum antibiotics. However, if there is an accumulation of purulent secretion (abscess), it is necessary to make an incision of the gland with a scalpel and perform drainage (extraction of puss from the wound using a drain).
Since this inflammation is often recurrent, it is advisable to perform a final surgical procedure after the acute phase subsides, which can be the following:
- Marsupialization – eversion (twisting) of the edges of the gland, which leads to permanent drainage of the gland or
- Extirpation (removal) of the Bartholin's gland through an incision on the inner side of the labia majora.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, and the patient is discharged home the next day. Due to the possibility of bleeding in the operated area, it is necessary that the patient is spared physical exertion during the next two to three weeks. A sample of the removed gland is sent for pathohistological analysis.
A septum (vaginal partition) is a congenital anomaly of the vagina that can divide the vagina into two parts or exist in only one segment of the vagina. The partition of the birth canal can be laid longitudinally or transversely. Problems caused by the vaginal septum usually appear in adolescence, and are manifested in painful menstruation. Also in adolescence, pain usually occurs during sexual intercourse or a septum is discovered during a routine gynecological examination.
The birth canal septum can be corrected surgically under general anesthesia. In addition to the birth canal septum, anomalies of the development of the uterus are also common. That is why it is necessary to do a complete diagnostic treatment in order to detect the presence of other anomalies of the gynecological organs and to consider the need or the possibility of their simultaneous surgical correction.
Benign tumors can be sebaceous gland cysts, the Bartholin's gland cysts, and mucinous and inclusion cysts. In addition to cystic formations, solid benign tumors, such as fibromas, lipomas, hidradenomas and pigmented moles, are also seen.
Benign pubic tumors are most often manifested as painless swellings, sharply limited to the surrounding tissue. The surgical procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia, whereby the tumor must be removed in its entirety. The patient is discharged home the next day. The removed tumor is sent for pathohistological analysis.